Gregor mendel pea plant experiment pdf Barcaldine
Law Of Segregation Mendel Pea Plant Experiment Mendel’s Experiments Background In this web lab, students experiment with garden pea plants (Pisum sativum) as did Austrian monk Gregor Mendel (1822-1884). Mendel chose to experiment with peas because they possessed four important qualities: 1. Peas had been shown to be true-breeding (all offspring will have the same characteristic
Mendel’s Pea Plants
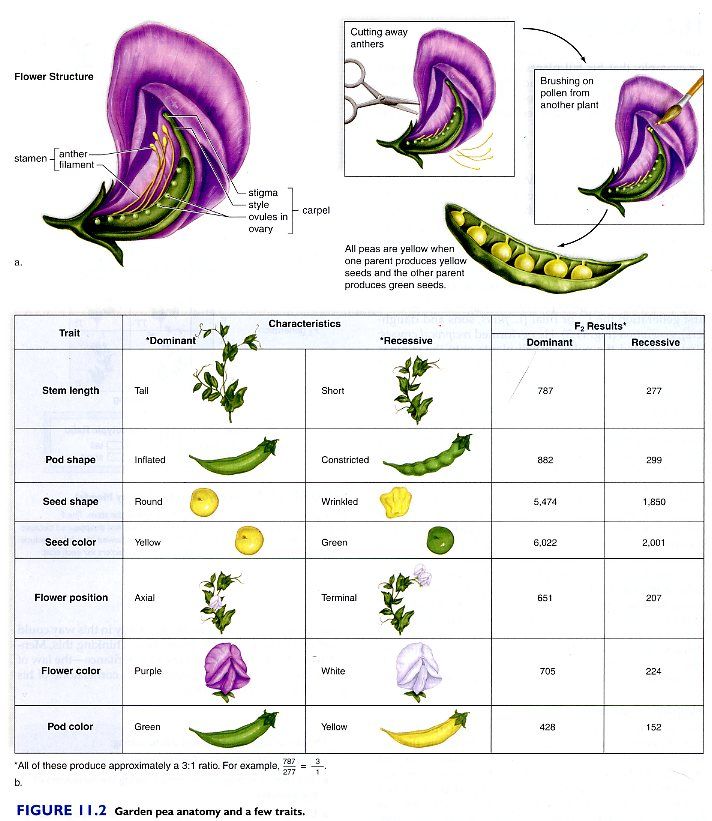
8 Best Johann Gregor Mendel images Genetics Life. Gregor Mendel was a 19th-century pioneer of genetics who today is remembered almost entirely for two things: being a monk and relentlessly studying different traits of pea plants. Born in 1822 in Austria, Mendel was raised on a farm and attended the University of Vienna in Austria's capital city., plant; Mendel studied numerous other pea plant traits, such as seed shape, seed color, flower color, pod shape, pod color, and the position of the pods. When Mendel studied the color of the flowers on the pea plants (purple or white) he saw the same effect. The color of the flowers did not blend together –.
EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT-HYBRIDISATION *. BY GREGOR MENDEL. (Read at the Meetings of the 8th February and 8th March, 1865.) INTRODUCTORY REMARKS. EXPERIENCE of artificial fertilisation , such as is effected with ornamental plants in order to obtain new variations in colour, has led to the experiments which will here be On Biography.com, learn more about Gregor Mendel, the 19th century monk whose experiments with pea plants led to some of the founding principles of genetics and theories of heredity—though the
22/02/2016 · Video is for educational purposes (8th grade Science) Information from CK-12, video clips from youtube, and images from CK-12 & google images. Gregor Mendel’s famous article is not a scientific paper in the usual sense, but a lecture presented to the Natural History Society of Brünn in 1865. The full results of his research were never published, but the portion that he did include, coupled with an extraordinary analysis of the data, makes his paper one of the landmarks of science. Mendel was fully aware that experiments in plant
EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT-HYBRIDISATION *. BY GREGOR MENDEL. (Read at the Meetings of the 8th February and 8th March, 1865.) INTRODUCTORY REMARKS. EXPERIENCE of artificial fertilisation , such as is effected with ornamental plants in order to obtain new variations in colour, has led to the experiments which will here be The Story of Gregor Mendel and his Peas This is the story of Gregor Mendel and how his pea experiments were used to study heredity. People had noticed for thousands of years that family resemblances were inherited from generation to generation, but no one knew how or why this pattern of heredity occurred. The study of genetics was soon created
Pea plants have both male and female reproductive organs. As a result, they can either self-pollinate themselves or cross-pollinate with another plant. In his experiments, Mendel was able to selectively cross-pollinate purebred plants with particular traits and observe the outcome over many generations. This was the basis for his conclusions "Alternative versions of genes account for variations in inherited characters." "For each character trait (ie: height, color, texture etc.) an organism inherits two genes, one from each parent
22/02/2016 · Video is for educational purposes (8th grade Science) Information from CK-12, video clips from youtube, and images from CK-12 & google images. Mendel’s Experiments Background In this web lab, students experiment with garden pea plants (Pisum sativum) as did Austrian monk Gregor Mendel (1822-1884). Mendel chose to experiment with peas because they possessed four important qualities: 1. Peas had been shown to be true-breeding (all offspring will have the same characteristic
An overview of Mendel's pea plant experiments. Introduces Gregor Mendel and illustrates the experiments he used to identify dominant and recessive traits.. Mendel's Pea Plants Worksheet 1. Between 1856 and 1863, a monk named Gregor Mendel experimented with pea plants. Mendel was fascinated with inheritance and sought to determine just how organisms passed on traits from one generation to the next. 2. Many scientists were hard at work trying to solve the mystery of inheritance. Studies were
02/03/2015 · An explanation of Gregor Mendel's genetic experiments on plants and how that relates to genetics today. Mendel’s pea plant experiments to learn more about what occurs as information passes from one generation to the next. zSpace Activity Activity Questions Provided in Studio Answers may vary. Sample answers are provided below. 1. Between 1856 and 1863 , a monk named Gregor Mendel experimented with pea plants. Mendel was
The Mendel Pea Experiment really was a ground-breaking piece of research. The Law of Segregation is the base from which genetic science developed. Whilst there are other processes at work, the Mendel Pea Experiment was the first to examine the processes behind heritable characteristics. Gregor Mendel is best known for his work with his pea plants in the abbey gardens. He spent about seven years planting, breeding and cultivating pea plants in an experimental part of the abbey garden that was started by the previous abbot. Through meticulous record-keeping, Mendel's experiments with pea plants became the basis for modern genetics.
On Biography.com, learn more about Gregor Mendel, the 19th century monk whose experiments with pea plants led to some of the founding principles of genetics and theories of heredity—though the An overview of Mendel's pea plant experiments. Introduces Gregor Mendel and illustrates the experiments he used to identify dominant and recessive traits..
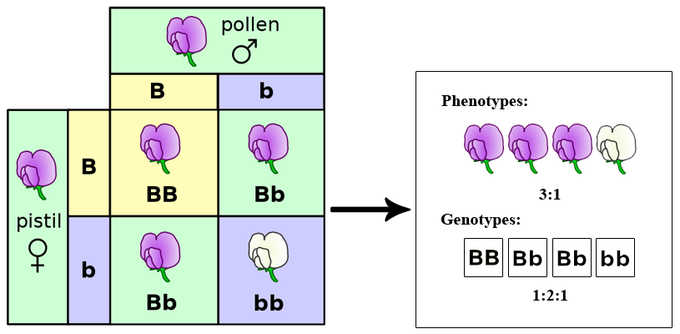
02/03/2015 · An explanation of Gregor Mendel's genetic experiments on plants and how that relates to genetics today. Mendel then pollinated each plant in the second generation with itself, and he found that one plant with yellow peas gave only plants with yellow peas, while others continued to give plants showing the 3:1 ratio. The plant with green peas gave only plants with green peas. This is the basis for Mendel’s law of segregation. Gregor Mendel Pea Plant Experiments Essay Assignments.
The Mendel Pea Experiment really was a ground-breaking piece of research. The Law of Segregation is the base from which genetic science developed. Whilst there are other processes at work, the Mendel Pea Experiment was the first to examine the processes behind heritable characteristics. Methods and Logic: Gregor Mendel Experiments in Plant Hybridization Cloe Pogoda 2-19-14. Mendel. Mendel • Johann Mendel was born into an ethnic German family in 1822. • He spent his early youth in that rural setting, until age 11, when a local schoolmaster who was impressed with his aptitude for learning recommended that he be sent to secondary school to continue his education. • Upon
Mendel’s Experiments EDC
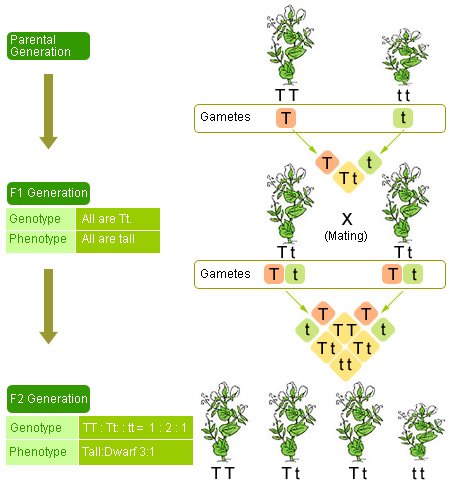
Gregor Mendel Life Pea Plant Experiments & Timeline. In one experiment, Mendel cross-pollinated smooth yellow pea plants with wrinkly green peas. (The organisms that are used as the original mating in an experiment are called the parental generation and are marked by P in science textbooks). Every single pea in the first generation crop (marked as f1) was as yellow and as round as was the yellow, round parent., The Forms of the Hybrid One of the most influential and important scientific works ever written, the 1865 paper Experiments in Plant Hybridisation was all but ignored in its day, and its author, Austrian priest and scientist GREGOR JOHANN MENDEL (18221884), died before seeing the dramatic long-term impact of his work, which was rediscovered at.
12 Mendel's Experiments and Heredity Biology LibreTexts. Mendel’s Experiment and Laws. In the 1860’s, an Austrian monk named Gregor Mendel introduced a new theory of inheritance based on his experimental work with pea plants. Mendel believed that heredity is the result of discrete units of inheritance, and every single unit (or gene) was independent in its actions in an individual’s genome., Mendel's life, experiments, and pea plants. How Austrian monk Gregor Mendel laid the foundations of genetics. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having ….
Mendel's Experiment and Laws Molecular Biology
Explanation of Mendel's work UCSF Tetrad Program. Published on The Embryo Project Encyclopedia (https://embryo.asu.edu) "Experiments in Plant Hybridization" (1866), by Johann Gregor Mendel [1] By: Andrei, Amanda Keywords: Mendel's experiment [2] Mendel's laws [3] During the mid-nineteenth century, Johann Gregor Mendel experimented with pea plants to develop a theory of inheritance. https://hif.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gregor_Mendel EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT-HYBRIDISATION *. BY GREGOR MENDEL. (Read at the Meetings of the 8th February and 8th March, 1865.) INTRODUCTORY REMARKS. EXPERIENCE of artificial fertilisation , such as is effected with ornamental plants in order to obtain new variations in colour, has led to the experiments which will here be.
gregor mendel s experiments on plant hybrids Download gregor mendel s experiments on plant hybrids or read online books in PDF, EPUB, Tuebl, and Mobi Format. Click Download or Read Online button to get gregor mendel s experiments on plant hybrids book now. This site is like a library, Use search box in the widget to get ebook that you want. Mendel's Pea Plants Worksheet 1. Between 1856 and 1863, a monk named Gregor Mendel experimented with pea plants. Mendel was fascinated with inheritance and sought to determine just how organisms passed on traits from one generation to the next. 2. Many scientists were hard at work trying to solve the mystery of inheritance. Studies were
An overview of Mendel's pea plant experiments. Introduces Gregor Mendel and illustrates the experiments he used to identify dominant and recessive traits.. The 3 laws of Mendel they are the most important statements of biological inheritance. Gregorio Mendel, a monk and Austrian naturalist, is considered the father of Genetics. Through his experiments with plants, Mendel discovered that certain traits were inherited following specific patterns.
Mendel’s Experiment and Laws. In the 1860’s, an Austrian monk named Gregor Mendel introduced a new theory of inheritance based on his experimental work with pea plants. Mendel believed that heredity is the result of discrete units of inheritance, and every single unit (or gene) was independent in its actions in an individual’s genome. Mendel made the observation that pea plants had characteristics that varied from plant to plant. He carried out experiments crossing (mating) plants with different characteristics. By observing
The Mendel Pea Experiment really was a ground-breaking piece of research. The Law of Segregation is the base from which genetic science developed. Whilst there are other processes at work, the Mendel Pea Experiment was the first to examine the processes behind heritable characteristics. Download Gregor Mendel in PDF and EPUB Formats for free. Gregor Mendel Book also available for Read Online, mobi, docx and mobile and kindle reading.
Mendel’s experiments on peas. Key principles of genetics were developed from Gregor Mendel’s ground-breaking experiments on inheritance in the 1860s. Mendel cross-bred pure lines of pea plants (Pisum sativum) and recorded the inheritance of visible traits, such as … Introduces Mendel's study of genetics. Pea Plants. Introduces Gregor Mendel and illustrates the experiments he used to identify dominant and recessive traits.. % Progress . MEMORY METER. This indicates how strong in your memory this concept is. Practice. Preview
plant; Mendel studied numerous other pea plant traits, such as seed shape, seed color, flower color, pod shape, pod color, and the position of the pods. When Mendel studied the color of the flowers on the pea plants (purple or white) he saw the same effect. The color of the flowers did not blend together – Mendel’s experiments on peas. Key principles of genetics were developed from Gregor Mendel’s ground-breaking experiments on inheritance in the 1860s. Mendel cross-bred pure lines of pea plants (Pisum sativum) and recorded the inheritance of visible traits, such as …
An overview of Mendel's pea plant experiments. Introduces Gregor Mendel and illustrates the experiments he used to identify dominant and recessive traits.. The Forms of the Hybrid One of the most influential and important scientific works ever written, the 1865 paper Experiments in Plant Hybridisation was all but ignored in its day, and its author, Austrian priest and scientist GREGOR JOHANN MENDEL (18221884), died before seeing the dramatic long-term impact of his work, which was rediscovered at
16170. Genes don't blend. DNAFTB Animation 3: Gregor Mendel explains that breeding short and tall pea plants didn't produce a medium-sized plant. Mendel then pollinated each plant in the second generation with itself, and he found that one plant with yellow peas gave only plants with yellow peas, while others continued to give plants showing the 3:1 ratio. The plant with green peas gave only plants with green peas. This is the basis for Mendel’s law of segregation. Gregor Mendel Pea Plant Experiments Essay Assignments.
Mendel’s pea plant experiments to learn more about what occurs as information passes from one generation to the next. zSpace Activity Activity Questions Provided in Studio Answers may vary. Sample answers are provided below. 1. Between 1856 and 1863 , a monk named Gregor Mendel experimented with pea plants. Mendel was 16170. Genes don't blend. DNAFTB Animation 3: Gregor Mendel explains that breeding short and tall pea plants didn't produce a medium-sized plant.
Mendel’s Experiment and Laws. In the 1860’s, an Austrian monk named Gregor Mendel introduced a new theory of inheritance based on his experimental work with pea plants. Mendel believed that heredity is the result of discrete units of inheritance, and every single unit (or gene) was independent in its actions in an individual’s genome. plant; Mendel studied numerous other pea plant traits, such as seed shape, seed color, flower color, pod shape, pod color, and the position of the pods. When Mendel studied the color of the flowers on the pea plants (purple or white) he saw the same effect. The color of the flowers did not blend together –
The 3 laws of Mendel they are the most important statements of biological inheritance. Gregorio Mendel, a monk and Austrian naturalist, is considered the father of Genetics. Through his experiments with plants, Mendel discovered that certain traits were inherited following specific patterns. Mendel’s pea plant experiments to learn more about what occurs as information passes from one generation to the next. zSpace Activity Activity Questions Provided in Studio Answers may vary. Sample answers are provided below. 1. Between 1856 and 1863 , a monk named Gregor Mendel experimented with pea plants. Mendel was
Pea Plants ( Read ) Biology CK-12 Foundation
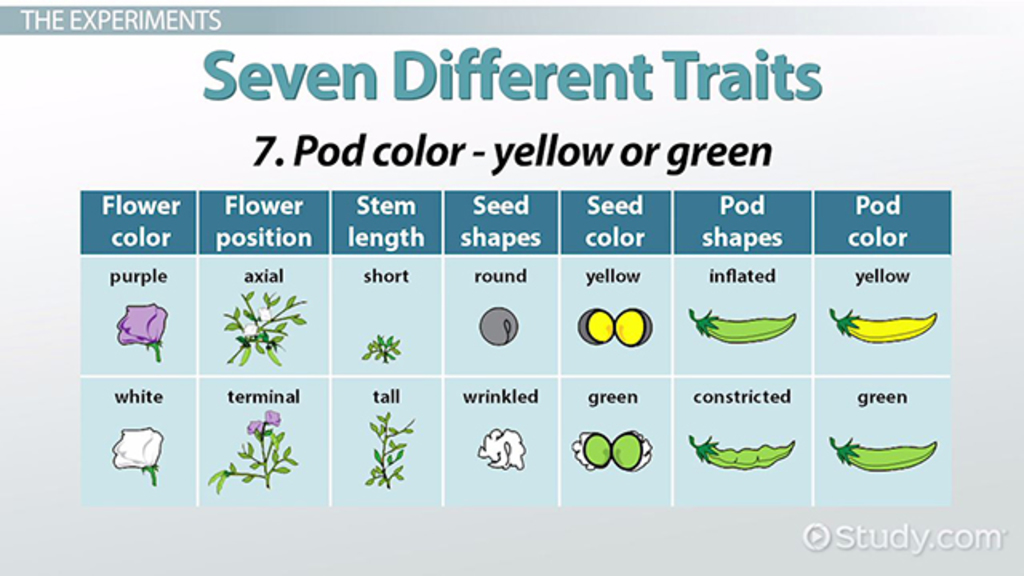
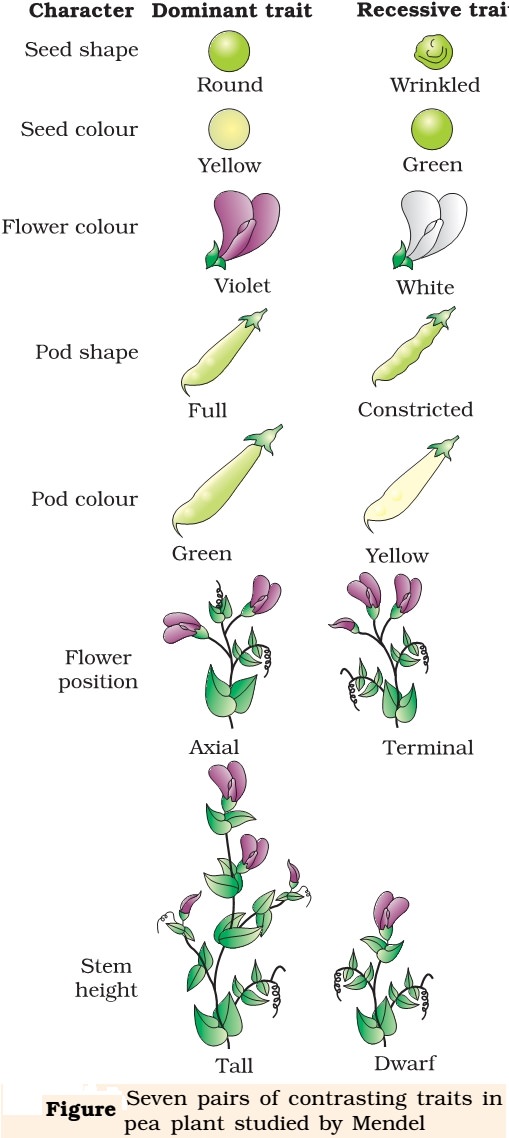
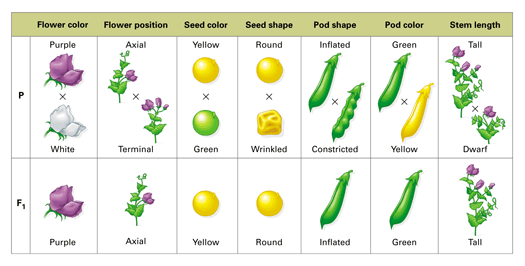
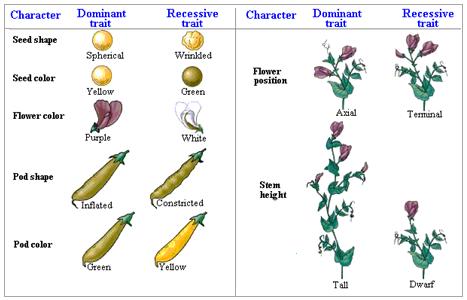
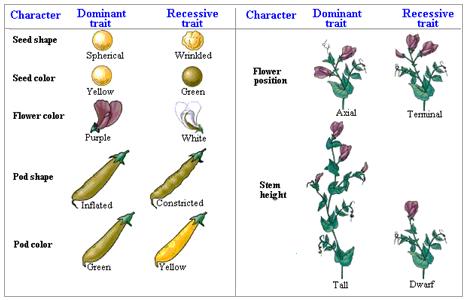
The Story of Gregor Mendel and his Peas Weebly. Pea plants have both male and female reproductive organs. As a result, they can either self-pollinate themselves or cross-pollinate with another plant. In his experiments, Mendel was able to selectively cross-pollinate purebred plants with particular traits and observe the outcome over many generations. This was the basis for his conclusions, Gregor studied seven traits of the pea plant: seed color, seed shape, flower position, flower color, pod shape, pod color, and the stem length. There were three major steps to Mendel's experiments: 1. First he produced a parent generation of true-breeding plants. He made these by self-fertilizing the plants until he knew they bred true to the.
Mendel's Pea Plants zSpace
5.1 mendel's experiments SlideShare. Methods and Logic: Gregor Mendel Experiments in Plant Hybridization Cloe Pogoda 2-19-14. Mendel. Mendel • Johann Mendel was born into an ethnic German family in 1822. • He spent his early youth in that rural setting, until age 11, when a local schoolmaster who was impressed with his aptitude for learning recommended that he be sent to secondary school to continue his education. • Upon, Mendel then pollinated each plant in the second generation with itself, and he found that one plant with yellow peas gave only plants with yellow peas, while others continued to give plants showing the 3:1 ratio. The plant with green peas gave only plants with green peas. This is the basis for Mendel’s law of segregation. Gregor Mendel Pea Plant Experiments Essay Assignments..
Gregor Mendel biography.pdf. Gregor Mendel biography.pdf. Sign In. Whoops! There was a problem previewing Gregor Mendel biography.pdf. Retrying. Because of Mendel’s work, the fundamental principles of heredity were revealed. 12.1: Mendel’s Experiments and the Laws of Probability In 1865, Mendel presented the results of his experiments with nearly 30,000 pea plants to the local Natural History Society. He demonstrated that traits are transmitted faithfully from parents to offspring
16170. Genes don't blend. DNAFTB Animation 3: Gregor Mendel explains that breeding short and tall pea plants didn't produce a medium-sized plant. Mendel's Pea Plants Worksheet 1. Between 1856 and 1863, a monk named Gregor Mendel experimented with pea plants. Mendel was fascinated with inheritance and sought to determine just how organisms passed on traits from one generation to the next. 2. Many scientists were hard at work trying to solve the mystery of inheritance. Studies were
Methods and Logic: Gregor Mendel Experiments in Plant Hybridization Cloe Pogoda 2-19-14. Mendel. Mendel • Johann Mendel was born into an ethnic German family in 1822. • He spent his early youth in that rural setting, until age 11, when a local schoolmaster who was impressed with his aptitude for learning recommended that he be sent to secondary school to continue his education. • Upon Mendel then pollinated each plant in the second generation with itself, and he found that one plant with yellow peas gave only plants with yellow peas, while others continued to give plants showing the 3:1 ratio. The plant with green peas gave only plants with green peas. This is the basis for Mendel’s law of segregation. Gregor Mendel Pea Plant Experiments Essay Assignments.
In one experiment, Mendel cross-pollinated smooth yellow pea plants with wrinkly green peas. (The organisms that are used as the original mating in an experiment are called the parental generation and are marked by P in science textbooks). Every single pea in the first generation crop (marked as f1) was as yellow and as round as was the yellow, round parent. After initial experiments with pea plants, Mendel settled on studying seven traits that seemed to be inherited independently of other traits: seed shape, flower color, seed coat tint, pod shape, unripe pod color, flower location, and plant height. He first focused …
The 3 laws of Mendel they are the most important statements of biological inheritance. Gregorio Mendel, a monk and Austrian naturalist, is considered the father of Genetics. Through his experiments with plants, Mendel discovered that certain traits were inherited following specific patterns. On Biography.com, learn more about Gregor Mendel, the 19th century monk whose experiments with pea plants led to some of the founding principles of genetics and theories of heredity—though the
Published on The Embryo Project Encyclopedia (https://embryo.asu.edu) "Experiments in Plant Hybridization" (1866), by Johann Gregor Mendel [1] By: Andrei, Amanda Keywords: Mendel's experiment [2] Mendel's laws [3] During the mid-nineteenth century, Johann Gregor Mendel experimented with pea plants to develop a theory of inheritance. Gregor Mendel is best known for his work with his pea plants in the abbey gardens. He spent about seven years planting, breeding and cultivating pea plants in an experimental part of the abbey garden that was started by the previous abbot. Through meticulous record-keeping, Mendel's experiments with pea plants became the basis for modern genetics.
On Biography.com, learn more about Gregor Mendel, the 19th century monk whose experiments with pea plants led to some of the founding principles of genetics and theories of heredity—though the 01/10/2016 · The sixth experiment has almost an identical result; in the others the ratio fluctuates more or less, as must be expected given the small number of 100 experimental plants. The fifth experiment, which showed the largest deviation, was repeated and then, instead of …
Mendel’s Experiments Background In this web lab, students experiment with garden pea plants (Pisum sativum) as did Austrian monk Gregor Mendel (1822-1884). Mendel chose to experiment with peas because they possessed four important qualities: 1. Peas had been shown to be true-breeding (all offspring will have the same characteristic Mendel says, “Plant five pea plants and observe what they look like.” Click the Plant button. The animated Mendel will plant and water five pea plants. You can observe the color of the pea pod, the shape of the pod, and the color and form of the ripe seed by rolling over the plants with your cursor. Now, you can experiment with plant
01/10/2016 · The sixth experiment has almost an identical result; in the others the ratio fluctuates more or less, as must be expected given the small number of 100 experimental plants. The fifth experiment, which showed the largest deviation, was repeated and then, instead of … Gregor Mendel Experiment. Gregor Mendel was an Austrian Monk, who postulated the laws of hereditary through his pea plant experiments. Mendel experimented with over 30 thousand pea plants in a span of 15 years, and studied the various influences of heredity. More..
Gregor Mendel Experiment. Gregor Mendel was an Austrian Monk, who postulated the laws of hereditary through his pea plant experiments. Mendel experimented with over 30 thousand pea plants in a span of 15 years, and studied the various influences of heredity. More.. Mendel’s pea plant experiments to learn more about what occurs as information passes from one generation to the next. zSpace Activity Activity Questions Provided in Studio Answers may vary. Sample answers are provided below. 1. Between 1856 and 1863 , a monk named Gregor Mendel experimented with pea plants. Mendel was
Mendel's life, experiments, and pea plants. How Austrian monk Gregor Mendel laid the foundations of genetics. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having … 02/03/2015 · An explanation of Gregor Mendel's genetic experiments on plants and how that relates to genetics today.
"Experiments in Plant Hybridization" (1866) by Johann. Pea plants have both male and female reproductive organs. As a result, they can either self-pollinate themselves or cross-pollinate with another plant. In his experiments, Mendel was able to selectively cross-pollinate purebred plants with particular traits and observe the outcome over many generations. This was the basis for his conclusions, Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) is a now-famous monk and scientist from the Czech Republic who discovered the laws of inheritance. For eight years, he cultivated and classified hybridized pea plants. Mendel concluded that traits are inherited and statistically predictable in the next generation..
Basic Principles of Genetics Mendel's Genetics
Gregor Mendel Pea Plant Experiments Essay Assignments. 02/03/2015 · An explanation of Gregor Mendel's genetic experiments on plants and how that relates to genetics today., Mendel’s pea plant experiments to learn more about what occurs as information passes from one generation to the next. zSpace Activity Activity Questions Provided in Studio Answers may vary. Sample answers are provided below. 1. Between 1856 and 1863 , a monk named Gregor Mendel experimented with pea plants. Mendel was.
The 3 Laws of Mendel and the Experiments of the Peas

Gregor Mendel Wikipedia. Gregor Mendel was a 19th-century pioneer of genetics who today is remembered almost entirely for two things: being a monk and relentlessly studying different traits of pea plants. Born in 1822 in Austria, Mendel was raised on a farm and attended the University of Vienna in Austria's capital city. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Experiments_on_Plant_Hybridization Gregor studied seven traits of the pea plant: seed color, seed shape, flower position, flower color, pod shape, pod color, and the stem length. There were three major steps to Mendel's experiments: 1. First he produced a parent generation of true-breeding plants. He made these by self-fertilizing the plants until he knew they bred true to the.
Mendel made the observation that pea plants had characteristics that varied from plant to plant. He carried out experiments crossing (mating) plants with different characteristics. By observing Mendel’s Experiment and Laws. In the 1860’s, an Austrian monk named Gregor Mendel introduced a new theory of inheritance based on his experimental work with pea plants. Mendel believed that heredity is the result of discrete units of inheritance, and every single unit (or gene) was independent in its actions in an individual’s genome.
Because of Mendel’s work, the fundamental principles of heredity were revealed. 12.1: Mendel’s Experiments and the Laws of Probability In 1865, Mendel presented the results of his experiments with nearly 30,000 pea plants to the local Natural History Society. He demonstrated that traits are transmitted faithfully from parents to offspring After initial experiments with pea plants, Mendel settled on studying seven traits that seemed to be inherited independently of other traits: seed shape, flower color, seed coat tint, pod shape, unripe pod color, flower location, and plant height. He first focused …
02/03/2015В В· An explanation of Gregor Mendel's genetic experiments on plants and how that relates to genetics today. In one experiment, Mendel cross-pollinated smooth yellow pea plants with wrinkly green peas. (The organisms that are used as the original mating in an experiment are called the parental generation and are marked by P in science textbooks). Every single pea in the first generation crop (marked as f1) was as yellow and as round as was the yellow, round parent.
On Biography.com, learn more about Gregor Mendel, the 19th century monk whose experiments with pea plants led to some of the founding principles of genetics and theories of heredity—though the Gregor Mendel biography.pdf. Gregor Mendel biography.pdf. Sign In. Whoops! There was a problem previewing Gregor Mendel biography.pdf. Retrying.
01/10/2016 · The sixth experiment has almost an identical result; in the others the ratio fluctuates more or less, as must be expected given the small number of 100 experimental plants. The fifth experiment, which showed the largest deviation, was repeated and then, instead of … Mendel’s Experiments Background In this web lab, students experiment with garden pea plants (Pisum sativum) as did Austrian monk Gregor Mendel (1822-1884). Mendel chose to experiment with peas because they possessed four important qualities: 1. Peas had been shown to be true-breeding (all offspring will have the same characteristic
Mendel says, “Plant five pea plants and observe what they look like.” Click the Plant button. The animated Mendel will plant and water five pea plants. You can observe the color of the pea pod, the shape of the pod, and the color and form of the ripe seed by rolling over the plants with your cursor. Now, you can experiment with plant Mendel made the observation that pea plants had characteristics that varied from plant to plant. He carried out experiments crossing (mating) plants with different characteristics. By observing
The Forms of the Hybrid One of the most influential and important scientific works ever written, the 1865 paper Experiments in Plant Hybridisation was all but ignored in its day, and its author, Austrian priest and scientist GREGOR JOHANN MENDEL (18221884), died before seeing the dramatic long-term impact of his work, which was rediscovered at Gregor Mendel Experiment. Gregor Mendel was an Austrian Monk, who postulated the laws of hereditary through his pea plant experiments. Mendel experimented with over 30 thousand pea plants in a span of 15 years, and studied the various influences of heredity. More..
plant; Mendel studied numerous other pea plant traits, such as seed shape, seed color, flower color, pod shape, pod color, and the position of the pods. When Mendel studied the color of the flowers on the pea plants (purple or white) he saw the same effect. The color of the flowers did not blend together – plant; Mendel studied numerous other pea plant traits, such as seed shape, seed color, flower color, pod shape, pod color, and the position of the pods. When Mendel studied the color of the flowers on the pea plants (purple or white) he saw the same effect. The color of the flowers did not blend together –
02/03/2015В В· An explanation of Gregor Mendel's genetic experiments on plants and how that relates to genetics today. EXPERIMENTS IN PLANT-HYBRIDISATION *. BY GREGOR MENDEL. (Read at the Meetings of the 8th February and 8th March, 1865.) INTRODUCTORY REMARKS. EXPERIENCE of artificial fertilisation , such as is effected with ornamental plants in order to obtain new variations in colour, has led to the experiments which will here be
Mendel’s Experiment and Laws. In the 1860’s, an Austrian monk named Gregor Mendel introduced a new theory of inheritance based on his experimental work with pea plants. Mendel believed that heredity is the result of discrete units of inheritance, and every single unit (or gene) was independent in its actions in an individual’s genome. The history of genetics started with the work of the Augustinian friar Gregor Johann Mendel. His work on pea plants, published in 1866, described what came to be known as Mendelian inheritance. Many theories of heredity proliferated in the centuries before and for several decades after Mendel's work.
The Mendel Pea Experiment really was a ground-breaking piece of research. The Law of Segregation is the base from which genetic science developed. Whilst there are other processes at work, the Mendel Pea Experiment was the first to examine the processes behind heritable characteristics. Download Gregor Mendel in PDF and EPUB Formats for free. Gregor Mendel Book also available for Read Online, mobi, docx and mobile and kindle reading.